Top 10 Waste Water Treatment Methods You Should Know?
Waste water treatment methods are essential in managing our planet's water resources. According to the World Health Organization, over 80% of global wastewater is released untreated. This alarming statistic highlights the urgent need for effective treatment strategies. The growth of urban populations increases wastewater generation, emphasizing the importance of efficient treatment methods.
Various waste water treatment methods exist, from physical processes like sedimentation to advanced biological techniques. Reports from the United Nations indicate that investing in eco-friendly treatment options can reduce environmental impact. Yet many regions still rely on outdated systems, leading to pollution and health hazards.
Innovation is key in improving waste water treatment methods. However, countries face challenges in implementation due to costs and infrastructure gaps. Understanding and adopting better practices is critical. In a world with limited freshwater resources, effective waste water management can create a sustainable future.
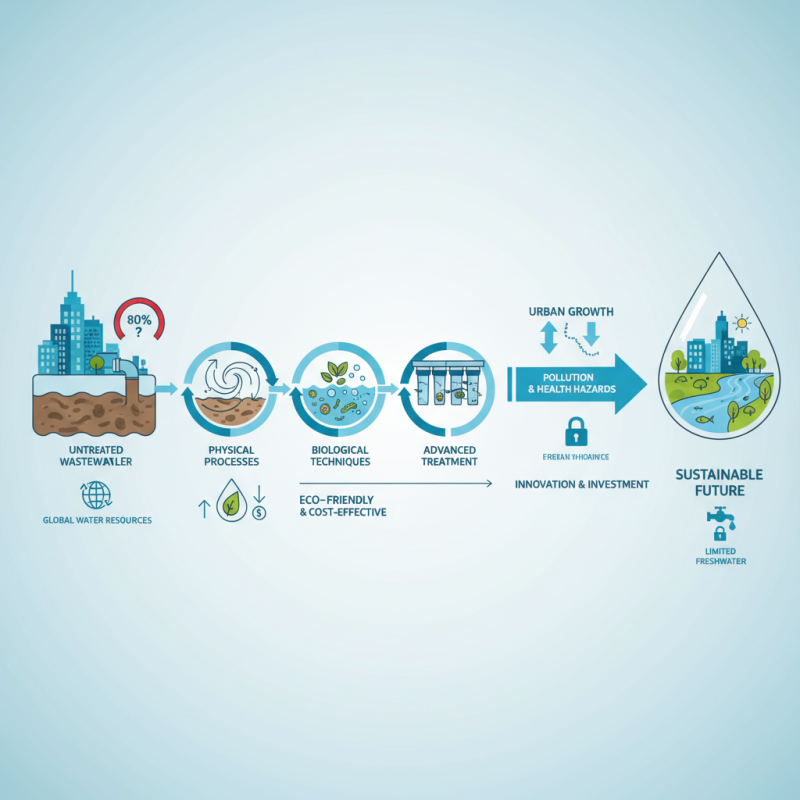
Overview of Waste Water Treatment Methods
Wastewater treatment is essential for environmental safety. Several methods exist, each with unique techniques and efficiency levels. Some common methods include physical, chemical, and biological treatments. Understanding these methods can help in choosing the right approach.
Physical treatment often involves sedimentation. This method allows solids to settle out of water. However, it may not remove all contaminants effectively. Chemical treatments use various agents to neutralize harmful substances. This can be beneficial but may lead to chemical residue issues.
Biological treatment leverages living organisms to break down pollutants. It’s effective but requires careful monitoring. The complexity of wastewater can lead to challenges in treatment efficiency. Many facilities face difficulties optimizing their processes. Balancing efficacy and environmental impact remains a significant concern in wastewater management. Users of these methods must constantly evaluate their strategies.
Top 10 Waste Water Treatment Methods
The following chart illustrates the efficiency of various waste water treatment methods based on their effectiveness in reducing contaminants.
Mechanical Treatment: Screening and Sedimentation
Mechanical treatment is an essential first step in wastewater treatment. It primarily involves screening and sedimentation processes. Screening efficiently removes larger debris, such as plastic and wood, from the wastewater. It prevents damage to downstream equipment. The screens are often made of metal or other durable materials, designed with various slot sizes to capture different particles.
Sedimentation follows screening. In this process, wastewater is allowed to sit in large tanks for some time. During this period, heavier solids settle at the bottom, forming sludge. The lighter materials float to the top, forming scum. Operators must regularly monitor and remove both sludge and scum. Neglecting this can lead to odor issues and reduced treatment efficiency.
While mechanical treatment is effective, it has limitations. It does not remove dissolved substances or pathogens. Thus, additional treatment steps are crucial. Despite its efficacy, some still overlook the importance of regular maintenance. Failing to do so can lead to more significant problems down the line, increasing costs and operational difficulties. Understanding these processes can improve wastewater management.
Top 10 Waste Water Treatment Methods You Should Know
| Method | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Treatment | Involves physical processes like screening and sedimentation to remove solids from wastewater. | Effective at removing large particles; simple operation. | Does not remove dissolved contaminants; only pre-treatment. |
| Biological Treatment | Uses microorganisms to decompose organic matter in wastewater. | Can effectively reduce organic load; environmentally friendly. | Requires management of microbial health; sensitive to changes in conditions. |
| Chemical Treatment | Utilizes chemical reactions to remove contaminants from wastewater. | Effective for removing heavy metals and pathogens; versatile. | Can produce harmful byproducts; chemical handling required. |
| Advanced Oxidation | Uses powerful oxidants to break down organic pollutants. | Highly effective for complex contaminants; can treat various types of water. | High operational costs; energy-intensive processes. |
| Membrane Filtration | Uses semi-permeable membranes to separate contaminants from water. | High removal efficiency; can filter out viruses and bacteria. | Membrane fouling; requires regular maintenance. |
| Electrocoagulation | Applies electrical currents to coagulate contaminants and facilitate their removal. | Effective for oily waste and heavy metals; quick process. | Energy consumption might be high; requires careful control. |
| Constructed Wetlands | Natural systems that use soil and plants to treat wastewater. | Sustainable and low-cost; enhances biodiversity. | Space-intensive; performance can vary with conditions. |
| Flotation | Utilizes air bubbles to lift contaminants to the surface for removal. | Effective for oil and grease removal; quick separation process. | Can be limited by water quality; requires proper bubble generation. |
| Sorption Techniques | Uses materials to adsorb contaminants from wastewater. | Versatile applications; effective for various pollutants. | Sorbent material disposal can be an issue; regeneration can be costly. |
Biological Treatment: Aerobic and Anaerobic Processes
Biological treatment processes are crucial in wastewater management. They can be broadly categorized into aerobic and anaerobic methods. Aerobic processes utilize oxygen to facilitate the breakdown of organic materials. This method often employs microorganisms that consume waste while generating carbon dioxide and water. The efficiency of aerobic treatment can reach up to 90% for organic removal, according to industry reports.
[Image]
Anaerobic processes, on the other hand, function without oxygen. They rely on specific bacteria to decompose organic matter, yielding biogas as a by-product. This biogas can be used for energy, providing a sustainable solution. Interestingly, anaerobic processes can reduce sludge volume significantly. However, they require more careful management and monitoring.
Tips: Regular maintenance of treatment systems is essential. Poor management can lead to malfunctions and inefficiencies. Always monitor the pH and temperature closely. Small fluctuations can affect bacterial activity significantly.
Both aerobic and anaerobic treatments have their advantages and challenges. While aerobic methods are faster, they can have higher operational costs. Anaerobic processes are more energy-efficient but may take longer to achieve the desired results. Wastewater treatment is not one-size-fits-all. Each method must be evaluated on its performance and suitability for specific waste types.
Chemical Treatment: Coagulation, Flocculation, and Disinfection
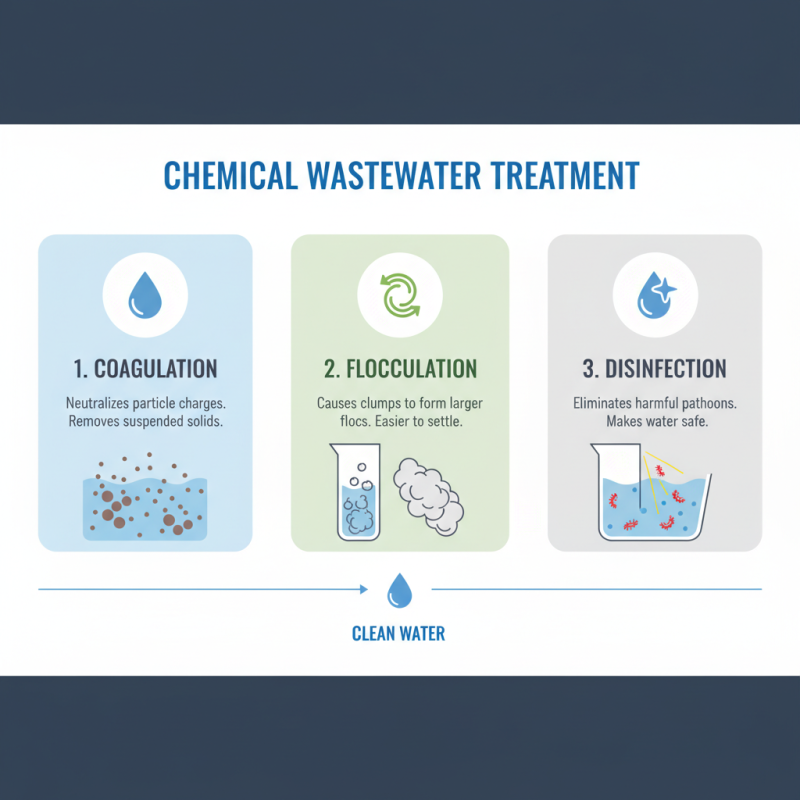
Chemical treatment is an essential part of wastewater management. The process typically involves three main steps: coagulation, flocculation, and disinfection. Coagulation begins with the addition of chemicals that neutralize the charges of particles in water. This step is crucial for removing suspended solids effectively.
Flocculation follows coagulation. During flocculation, small particles clump together, forming larger aggregates called flocs. This process often requires gentle mixing. Larger flocs are easier to remove in subsequent steps. Disinfection is the final step, targeting pathogens to ensure safe water release. Common methods include chlorination and UV light treatment.
**Tip:** Always monitor chemical dosages carefully. Too much can create secondary pollutants.
Maintaining optimal conditions is not easy. Variations in water quality can affect these processes. Adjustments may be necessary based on specific contaminants present.
**Tip:** Regular testing can help identify issues early.
Equipment maintenance is crucial. Leaks or malfunctioning devices can compromise treatment efficiency. Always check for performance records to identify any irregular patterns.
Advanced Treatment: Membrane Filtration and Reverse Osmosis
Membrane filtration and reverse osmosis are essential techniques in advanced wastewater treatment. These methods are known for their efficiency and effectiveness in removing pollutants. Membrane filtration uses semi-permeable membranes to separate contaminants. This process can filter out particles as small as viruses. It greatly enhances water quality, making it suitable for various applications.
Reverse osmosis (RO) is another powerful technique. It forces water through a membrane under pressure. This method strips away impurities, leaving behind clean water. RO can desalinate seawater, making it drinkable. However, it often requires considerable energy and can generate waste. Striking a balance between efficiency and sustainability is crucial.
Tips: Regular maintenance of filtration systems is vital. Clogged membranes reduce performance. Monitor water quality often to detect any changes early. Consider energy-efficient options to minimize costs. Investing in staff training can ensure optimal operation and maintenance.
Both membrane filtration and reverse osmosis can be costly to implement. But their benefits often outweigh these drawbacks. As technology advances, these methods may become even more accessible and cost-effective. Remember, continuous improvement in wastewater treatment is key to ensuring clean water for all.
Related Posts
-

Transforming Industrial Waste Water Treatment Solutions at the 138th Canton Fair 2025 for a Sustainable Future
-

Exploring Innovations in Sewer Treatment Plants at China Import and Export Fair 2025
-

10 Innovative Methods for Effective Waste Water Removal You Need to Know
-

Top 7 Wastewater Treatment Systems: Upgrade Your Water Management Solutions Today!
-

8 Best Sewage Treatment Plant Processes to Optimize Waste Management Efficiency
-

Top 2025 Innovations in Waste Water Treatment Process for Sustainable Solutions


